RBAC-BT
RBAC-based testing using Finite State Machines (FSM)
The RBAC-BT project is a GitHub repository with artifacts resulting from my MSc research project. The abstract of my MSc dissertation is shown below.
Access Control (AC) is a major pillar in software security. In short, AC ensures that only intended users can access resources and only the required access to accomplish some task will be given. In this context, Role Based Access Control (RBAC) has been established as one of the most important paradigms of access control. In an organization, users receive responsibilities and privileges through roles and, in AC systems implementing RBAC, permissions are granted through roles assigned to users. Despite the apparent simplicity, mistakes can occur during the development of RBAC systems and lead to faults or either security breaches. Therefore, a careful verification and validation process becomes necessary.
Access control testing aims at showing divergences between the actual and the intended behavior of access control mechanisms. Model Based Testing (MBT) is a variant of testing that relies on explicit models, such as Finite State Machines (FSM), for automatizing test generation. MBT has been successfully used for testing functional requirements; however, there is still lacking investigations on testing non-functional requirements, such as access control, specially in test criteria.
In this Master Dissertation, two aspects of MBT of RBAC were investigated: FSM-based testing methods on RBAC; and Test prioritization in the domain of RBAC.
At first, one recent (SPY) and two traditional (W and HSI) FSM-based testing methods were compared on RBAC policies specified as FSM models. The characteristics (number of resets, average test case length and test suite length) and the effectiveness of test suites generated from the W, HSI and SPY methods to five different RBAC policies were analyzed at an experiment.
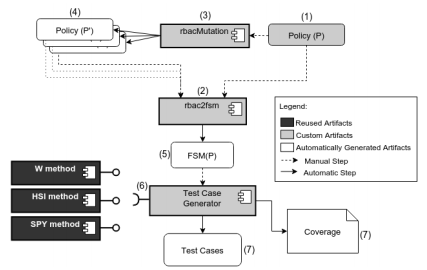
Later, three test prioritization methods were compared using the test suites generated in the previous investigation. A prioritization criteria based on RBAC similarity was introduced and compared to random prioritization and simple similarity.
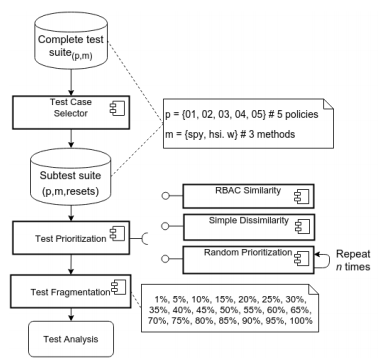
The obtained results pointed out that the SPY method outperformed W and HSI methods on RBAC domain. The RBAC similarity also achieved an Average Percentage Faults Detected (APFD) higher than the other approaches.